When to Use Noindex: Clean Up Thin or Duplicate Pages
Explains when and why to use the noindex tag – covering thin content, tag pages and staging environments.
🚫 Noindex Like a Pro: Protect Rankings, Save Crawl Budget
Using the noindex tag stops low-value pages from cluttering Google’s results and keeps your crawl budget focused on what matters.
🔍 Why the Noindex Tag Matters
- Removes thin or duplicative pages from the index
- Concentrates link equity on high-value content
- Speeds up future crawling by reducing index bloat
If unwanted pages are surfacing in search, a sprinkle of noindex is the neatest remedy.
⚙️ How Noindex Works
Add this meta tag inside the page’s <head>:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow">noindex keeps the page out of search results, while follow lets link equity flow to the pages you do want to rank.
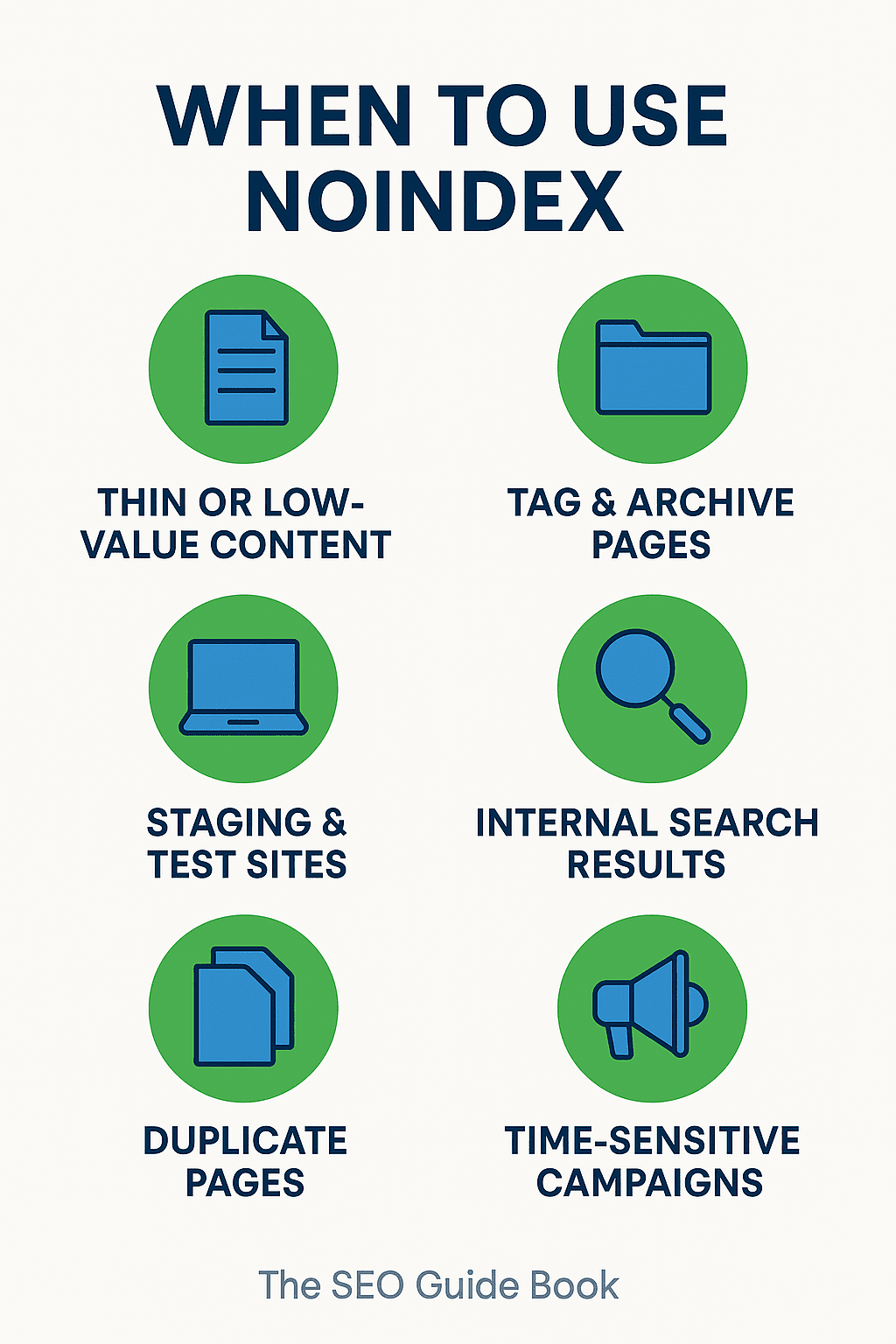
🚦 When to Reach for Noindex
📝 Thin or Low-Value Content
- Placeholder product pages
- Blog categories with just one or two posts
- Short press releases with no ongoing value
🏷️ Tag & Archive Pages
WordPress auto-generates tag, author and date archives. Unless you optimise them, they’re near-duplicate link lists – noindex prevents them competing with real articles.
🛠️ Staging & Test Sites
Cloned environments on sub-domains can trigger duplicate-content warnings. Add noindex (or password protection) before they go public.
🔎 Internal Search Results
Landing users on ?s= or /search/ pages makes for a poor experience. Noindex these URLs.
📄 Duplicate Pages
- Printer-friendly versions
- Filter or sort parameters (e.g.
?sort=price) - Regional pages with identical copy
⏰ Time-Sensitive Campaigns
Switch seasonal pages (e.g. Black Friday) to noindex once the offer ends, then plan a redirect.
⛔️ When Not to Use Noindex
- Pages already earning organic traffic
- Evergreen content with backlinks
- Core conversion pages (products, sign-up forms)
- Anything you intend to rank now or later
📝 Implementation Checklist
- Crawl the site to spot thin, duplicate or staging pages.
- Prioritise URLs with zero traffic and no backlinks.
- Add
noindex, followvia your CMS, template or server header. - Fetch & Inspect in Google Search Console to confirm.
- Monitor the “Excluded → Page with ‘noindex’ tag” report for peace of mind.
🎯 Key Takeaways
- Noindex is quick, reversible and keeps low-value pages out of search.
- Pair noindex with solid internal linking so equity still flows.
- The cleaner your index, the clearer your ranking signals.
✅ Final Thought: Tidiness Beats Bloat
A website is a bit like a shopfront. Customers should see polished displays, not the storeroom clutter. Every thin tag page, half-finished product, or dusty press release you leave indexed is a distraction for both search engines and users.
By applying the noindex tag strategically you sweep away those distractions and put the spotlight on what truly deserves attention. Your crawl budget stretches further, perceived quality rises, and high-value pages climb because the signal-to-noise ratio improves. In short, noindex is not about hiding weak pages – it’s about housekeeping that lets your strongest content shine.
“A tidy index is like a tidy shopfront—no one should be rummaging through your stockroom. Use noindex to show only what’s worth selling.”
– David Roche
💬 What the Experts Are Saying
- Lily Ray: “Noindexing thin archives can lift overall site quality scores and speed up recrawls.”
- Tom Critchlow: “Think of noindex as pruning: cut the weak branches so the healthy ones get more light.”
- Aleyda Solis: “One of the fastest wins for SMEs is cleaning index bloat—noindex delivers results without touching design or code.”
📝 Recap and Clarify: Post-Specific FAQs
What does a noindex tag do?
The noindex tag tells search engines not to include a specific page in their index. This prevents the page from appearing in search results.
When should I use the noindex tag?
Use it on low-value pages like thin content, duplicate tag/category pages, internal search results, and staging or development pages.
Is noindex good for SEO?
Yes. Noindexing irrelevant or poor-quality pages helps Google focus on your valuable content, improving crawl efficiency and overall SEO.
What’s the difference between noindex and robots.txt disallow?
Noindex tells Google not to index a page, but it still allows crawling. Robots.txt disallow blocks crawling, so Google might not see the noindex tag.
Can I use noindex on paginated pages?
Yes, especially if the paginated pages offer little standalone value. But be cautious—it can affect the discoverability of linked content.
Should I noindex old blog posts?
Only if they are thin, outdated, and not worth updating. Valuable or evergreen posts should be refreshed and kept indexed.
Can I noindex a page temporarily?
Yes. You can use noindex during development or updates and remove it once the page is ready to rank in search results.
How do I apply a noindex tag in WordPress?
Most SEO plugins like Yoast or Rank Math offer a simple checkbox to add a noindex meta tag to individual posts or pages.
What’s a common mistake when using noindex?
Blocking a page via robots.txt while also using noindex. If the page can’t be crawled, Google won’t see the noindex instruction.
Does removing noindex automatically reindex my page?
No. After removing the noindex tag, you should request indexing via Google Search Console to speed up the process.